Have you tried to get rid of your MRSA infection, only to find it keeps coming back? You’ve likely used multiple types of antibiotics, spend hundreds, if not thousands of dollars. You can find the cure to it. in ‘Light therapy!’ Read about it, in detail, and know can light be of help?
What does MRSA stand for?
Commonly it is known a s ‘staph’ infection, and it shows up on the skin with red marks, lesions and sometimes boils. MRSA belongs to the large group of bacteria known as Staphylococci, often referred to as Staph.
MRSA is an abbreviation for Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus bacteria. This bacterium is known to cause skin infections along with many other types of infections. MRSA is called a “super bug” because the infections caused by this organism are resistant to many common antibiotics like the ones belonging to the beta-lactam family, including methicillin and penicillin.
How do I know that I am infected with MRSA?
The first symptoms of MRSA…… All Staph infections, including MRSA, will begin as small red bumps that look like pimples, boils or spider bites.It also might infect a surgical wound. You could detect it if that area of your body looks swollen, red, and painful or is filled with pus. Sometimes, a deep and painful abscess that requires medical intervention like surgical draining. Other signs for this infection are: Sty-It is the infection of eyelid gland , Carbuncles- These are infections larger than an abscess, usually with several openings to the skin , Impetigo- This is a skin infection with pus-filled blisters.
If MRSA infects the lungs and causes pneumonia, you might experience the following:
- Shortness of breath
- Fever
- Cough
- Chills
When an MRSA bacterium spreads deep into the body, it can cause infections in bones, joints, surgical wounds, the bloodstream, urinary tract, heart valves, and lungs. For some, this infection can be life-threatening.
You should be very careful if these symptoms are visible on your body as many people don’t take it seriously and mistake it for a spider bite. One major problem with MRSA is that many a times the skin infection can spread to other parts of the body as well. And when this happens, it leads to the development of more severe symptoms. In fact, spread of this bacterium to internal organs can become life-threatening. Therefore, you should never take any symptom lightly and consult the doctor right away.
How contagious is MRSA?
First of all, you should be well aware that it is a contagious disease. MRSA infection that spreads through direct contact with infected people, or by touching contaminated surfaces, however MRSA can also spread through air. People with active MRSA infections are obviously more contagious but even MRSA carriers who are not infected cab be a cause of spreading or causing infections.
The infection can spread so, you avoid:
- direct contact with another via a handshake
- common use of some item, such as bed linens, clothing, bathroom fixtures, or medical equipment
According to a Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) study published in the Journal of the American Medical Association Internal Medicine, life-threatening MRSA infections in healthcare settings decreased 54% between 2005 and 2011.While this decline is good news, MRSA has not been fully eradicated.In healthcare settings, MRSA has been known to cause bloodstream infections, pneumonia, and surgical site infections.
Infected skin (MRSA picture)
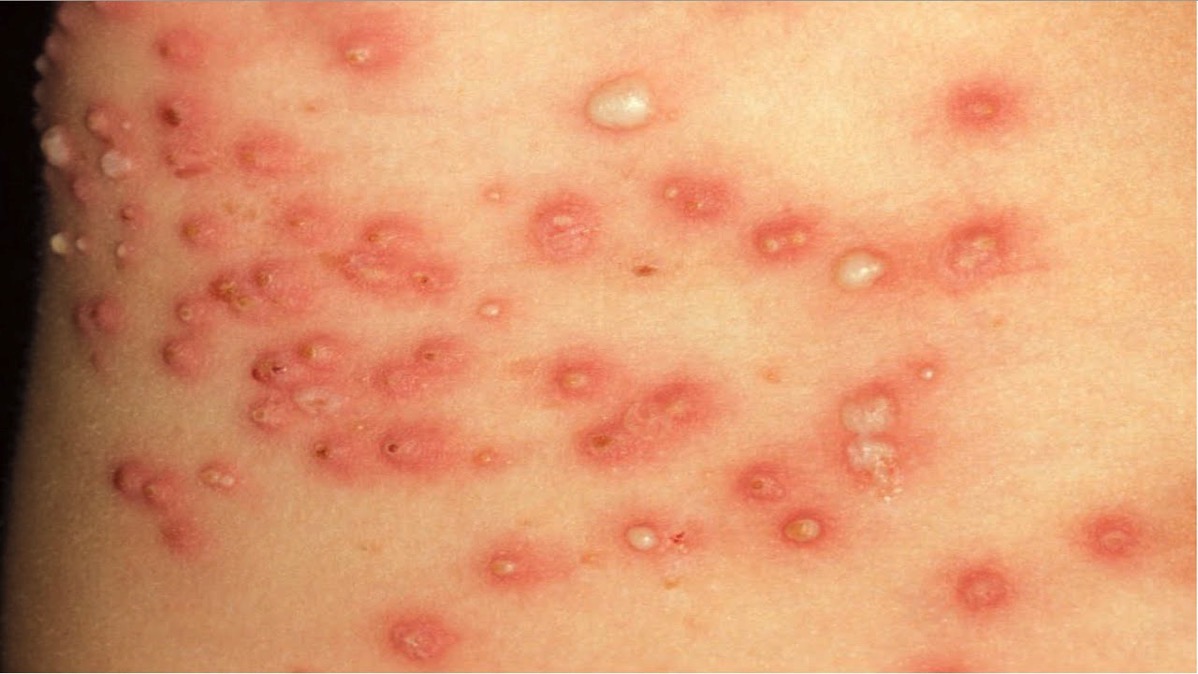
Can MRSA infection be fatal?
If you’ve ever thought that MRSa can kill you? You must be well aware and vigilant enough to treat it! Staph bacteria is one of the most common cause for skin infections in the United States. Most of the people, around 30% of them carry staph bacteria in their nose and it does not pose any danger to them or anyone else. But, when staph bacteria enter your body through a cut, they cause mild skin infection that can be treated easily. But it is true that it can be fatal!
It can invade the body’s bloodstream and release poisonous toxins. If the bacteria gets into the body through a wound or a break in the skin, it can cause life-threatening infections known as sepsis or blood poisoning which can cause dysfunctioning of vital organs. In severe cases of blood-poisoning known as septicaemia, the blood supply to vital organs such as the brain and heart is reduced. Statistics suggest: In 2007, the Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA) reported 17,000 deaths from HIV/AIDS, while Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus or MRSA killed 18,600 people.
Why is it so difficult to treat it?
The main problem being, infection causing bacteria (MRSA) have evolved to actively resist cer tain antibi otics.
It was 1961 when MRSA was first discovered in United Kingdom. This started when Methicillin antibiotics were introduced to treat Staphylococcus aureus (or “Staph”) infections, which at that time were already resistant to penicillin-type antibiotics. In its early years, Methicillin had been effective in treating Staph infections however, its potency to treat this infection eventually diminished when Staph learned to resist its effect. That’s when health care professionals began to be alarmed about the implications of these infections. And now, MRSA bacteria are resistant to many more antibiotics, and some strains of MRSA are resistant to ALL antibiotics.
Three factors contribute to its difficulty to treat it since,
- First, its pathogenicity indicates the bacteria can cause disease.
- Second, since MRSA shows resistance to many antibiotics, treatment options are limited.
- Third, MRSA is transmissible directly and indirectly through contact with infected patients and the surfaces they touch. Practicing stellar hand hygiene is very important and it will help to decrease, if not eliminate, MRSA’s spread.
Is MRSA Curable? OR Are there any methods to get rid of it naturally?
There is no complete ‘natural’ cure for MRSA. The fight with this bacterium continues life long ! However, there are certain natural foods that can help to boost your immunity. For example garlic is known to improve immunity levels. While there are certain natural antibiotics, or extracts that are known to mitigate or kill bacteria. In the name of alternative madicine for MRSA you might have heard about Manuka honey, Colloidal silver and Tea tree oil, since they are known to have antibiotic properties.
Since the causal bacteria behind MRSA is known to adapt to antibiotics and become resistant such that remedies become ineffective after a period of time. Research does not prove the complete effectiveness of any of them, but they have provided relief to some while to some they remained ineffective.
For example, 1. A research published by NCBI states the ineffectiveness of manuka honey to treat MRSA, which one was effective in treating this disease. 2. Another clinical review from NCBI documents that there is insufficient evidence to say that tea tree oil can eradicate MRSA.
Researchers agree to the fact that this infection, is only subsided and not treated by any of the natural remedies, or antibiotics, and is very stubborn as well as recurring! Thus, Staphylococcus aureus infections pose a significant health burden.Takin into consideration all modes of transmission and hygiene issues along with the resistance of bacterium against antibiotics a research at NCBI says Novel strategies for the prevention of recurrent SSTI (Skin and soft tissue infections) are needed.
Blue Light: The bacteria Killer!
Search for novel strategies to treat MRSA has led to checking for the efficacy of Blue Light for this purpose. Yes, Blue light is known to have bactericidal properties!
It has been found that ‘Blue Light’ has anti microbial effect on a wide spectrum of bacteria (both gram positive and gram negative) as well as fungi. Not only this, but its importance in killing bacteria is very crucial since it also has the potential to kill ‘drug resistant bacteria’. Studies reveal that blue light has been very potent in resisting growth of leuconostoc, pseudomonas and bacillus species which reported to be resistant to the antibiotic Methicillin.
Paying special attention to MRSA (Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus). This bacteria since it is antibiotic resistant has the potential to cause life threatening infections in human beings. Intense blue light, preferably at 415nm, is better than red light for bacteria killing. (NCBI). Irradiation with blue light can help to Kill it!
There are strong reasons for using ‘Blue Light’ for such infections:
We all have now become aware of the fact that, over dependency on Antibiotics leads to the bacterial strains becoming resistant! The extensive use of antibiotics is the single most important factor leading to drug resistance, says NCBI . A novel light-based approach, antimicrobial blue light (aBL), has attracted increasing attention due to its intrinsic antimicrobial effect without the involvement of exogenous photosensitizers.
The American society of Microbiology, also affirms the same about treating infectious bacteria with ‘Blue LEDs’ and also states that unlike bacteria killing Ultra Voilet Light, Blue light isn’t harmful to the skin cells. (According to a clinical trial conducted on mice)
There are ample of research based findings about ‘Blue Light’ and researches that support its efficacy in being able to kill MRSA ( or other drug resistant bacteria). Suggested readings:
- Blue Light destroys Methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus. (1)
- Blue light eliminates community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in infected mouse skin abrasions. (2)
- In vitro bactericidal effects of 405-nm and 470-nm blue light. (3)
- Blue Light Destroys Antibiotic-resistant Staph Infection. (4)
- In vitro bactericidal activity of blue light (465 nm) phototherapy. (5)
What we can conclude is, that ‘Blue light’ is the best alternative medicine to treat staph infections!
How can it be used?
Recent studies have shown that all bacteria, including MRSA are highly sensitive (i.e. can be killed by) light that is between 405-nm and 470-nm. Light in this spectrum is blue in color, hence the name.”Irradiation with [blue] light energy is a practical and inexpensive alternative to treating MRSA without using any antibiotics which mostly fail to give lasting results.” Enwemeka and colleagues concluded
What you can do is… You could contact a medical center that offers blue light therapy for their patients such as a beauty therapy clinic and ask them if they are prepared to treat your MRSA infection with one of their devices. Bear in mind though that due to the fact that MRSA is highly contagious they may well refuse.
If that happens don’t despair because there is another option…Blue light therapy devices can be used at home! These can be easily purchased online.
You don’t need to do a lot of hard work finding a suitable device, and neither will nay one cause a big dent in your pocket… Any LED blue light bulb/device that is between 405nm and 470nm with an energy density of 55 J/cm2 should do the trick.
There is no special skill that you need, for treating your infections with ‘Blue Light’. you just need to shine the light using your preferred device, over the affected area, for about 15 to 2o minutes, or a sit may be needed to heal your infections or lesions. Since the ‘Blue Light used’ is UV free, it poses no safety concerns! This method, relieves you of any concerns related to the bacteria becoming resistant and does not harm the nearby tissues too!
UV lamp for skin treatment: Can it be used for MRSA ?
UV C: UVC (200–280 nm). UVC (termed germicidal UV) in the range of 262nm is the most lethal range of wavelength, as it gets absorbed by the DNA and RNA of the micro-organisms changing the structure of nucleic acids. It has been observed that as compared to conventional UV lamp the 207nm UV light efficiently killed MRSA, and did not produce human cell killing.
The study concluded that 207nm light irradiation efficiently kills the bacteria without causing any mutagenic effect in human cells, signifying that 207nm UV light irradiation may be a potential therapeutic application in infectious surgical site, including drug resistant bacteria. This emphasised the role of UVC irradiation as an adjuvant therapy for chronic wound infected with MRSA. So, UV lamps can be used, but we do not recommend you to do so. Let’s find out why?
UV LIGHT or BLUE LIGHT? Which is better?
Our result of ‘Blue Light; being a much better and favourable option, is due to two most important points. (Reference)
1. It is well accepted that blue light is much less detrimental than UVC irradiation to host cells.
EXPLANATION: Blue light exhibits a broad-spectrum antimicrobial effect against both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria without the addition of exogenous photosensitizers and it has been suggested as an alternative treatment modality for treating MRSA infections [112]. When compared to UV irradiation, blue light has been accepted to be much less detrimental to mammalian cells.
2. Since the microbial cells can develop some resistance to UV irradiation, it would be worthy to consider whether resistance can be induced to blue light in microbial cells. While, MRSA bacterium is not resistant to blue light.
EXPLANATION: Antimicrobial resistance is now a global problem, causing bacterial infections that cannot be treated with existing antibiotics. Many physicians are concerned that several bacterial infections soon may become untreatable. As a result, there is a pressing need for the development of alternative treatment regimens, to which bacteria will not be easily able to develop resistance (eg, antimicrobial blue light therapy), for multidrug-resistant wound infections.
EDITOR”S NOTE: You need not be despaired, since there is a proven safe and effective cure of MRSA. Check out for the best ‘Blue Light’ devices’, so that you can treat yourself at home without posing any danger to yourself or any chance of passing it on to others!
References:
http://healthywithhoney.com/what-kills-staphylococcus-aureus-does-manuka-honey-kill-mrsa/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15824699
https://www.medicinenet.com/is_mrsa_contagious/article.htm#what_is_mrsa
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4837971/
https://digitalcommons.unl.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=2101&context=usdaarsfacpub
https://www.photonics.com/a55954/Blue-light_phototherapy_kills
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19196103
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17199466
https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007%2F978-0-387-71809-5_4
https://www.staph-infection-resources.com/info/contagious/
https://academic.oup.com/cid/article/47/2/176/357090
https://www.mercola.com/Downloads/bonus/mrsa-virus/report.htm
https://www.express.co.uk/life-style/health/717343/what-is-MRSA-deadly-superbug-antibiotics-sepsis
https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2013/11/131113144109.htm
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4552962/
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-017-05000-0
http://jcm.asm.org/content/51/1/202.full
http://theboilbible.com/blue-light-therapy-is-the-biggest-development-in-mrsa-treatment-in-years/
https://www.webmd.com/a-to-z-guides/news/20090204/blue-light-kills-mrsa
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12426452
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12426452
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3831650/


